With the continuous optimization of the global energy structure, natural gas, as a clean energy, has been increasingly valued by various countries. As one of the core facilities for natural gas transportation, natural gas standard stations play an important role. In natural gas standard stations, compressors are key equipment, and their types and performance directly affect the efficiency and safety of natural gas transportation. Next, Anhui Hongshen Energy Equipment will introduce the common types of natural gas standard station compressors and their importance in practical applications.
Basic concepts of natural gas standard station compressors
Natural gas compressors compress the volume of natural gas through mechanical energy, thereby increasing its pressure and density to meet the needs of long-distance and high-pressure transportation. In natural gas standard stations, the role of compressors is to keep the gas at a certain pressure during transportation, ensuring that natural gas can be smoothly transported to various consumer terminals.
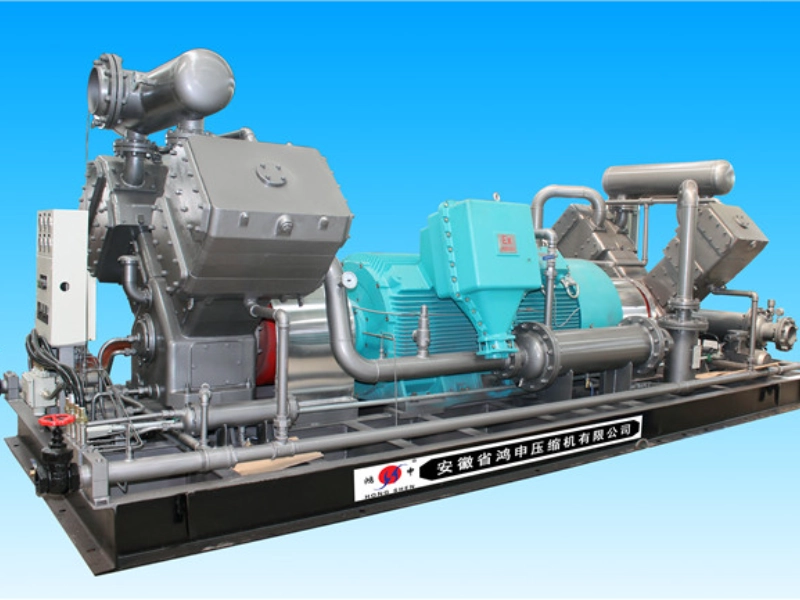
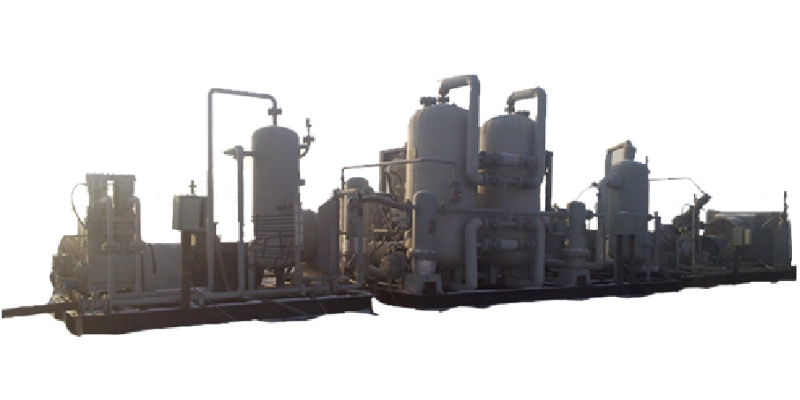
Natural gas standard station compressor equipment can be divided into different types according to different working principles, structures and application scenarios. The most common ones are piston compressors, screw compressors, centrifugal compressors, etc.
Piston compressors
Piston compressors are a traditional and common natural gas compression equipment, and their working principle is similar to that of an internal combustion engine in a car engine. The piston reciprocates in the cylinder, compressing the gas to increase its pressure.
Features:
Strong adaptability: It can adapt to a variety of gas types, especially when dealing with low-pressure natural gas, it has a good effect.
Wide pressure range: It is suitable for the compression needs of medium to high-pressure natural gas, and the pressure can reach up to 50MPa.
Simple structure: Due to its simple mechanical structure, it is relatively easy to maintain.
Applicable scenarios:
Piston compressors are suitable for small and medium-sized natural gas standard stations, especially when the natural gas pressure does not need to be very high, and are often used for some short-distance gas transportation.
Screw compressors
Screw compressors use a pair of rotating screws to compress gas. Its working principle is to form a closed cavity between the screws, and compress the gas to a higher pressure through the rotation of the screw.
Features:
High efficiency: Compared with piston compressors, screw compressors have higher efficiency, especially when dealing with high-flow natural gas.
Good stability: It has stable operation, can work continuously for a long time, and has low noise.
Wide applicability: It can compress a variety of gases and is widely used in the compression of low-pressure and medium-pressure natural gas.
Applicable scenarios:
Screw compressors are mostly used in larger natural gas standard stations, especially when they need to handle higher flow rates and higher stability requirements, and they can better meet the needs of long-term operations.
Centrifugal compressors
Centrifugal compressors generate centrifugal force through high-speed rotation of the rotor, accelerate the gas and compress it through the reducer. This type of compressor usually has a very high flow rate.
Features:
High flow rate: The biggest advantage of centrifugal compressors is that they can handle large flows of natural gas, which is suitable for large natural gas transmission systems.
High efficiency: The equipment can provide high-pressure natural gas at low energy consumption and has a high energy efficiency ratio.
Complex maintenance: Compared with other types of compressors, the structure of centrifugal compressors is more complex and requires professional technology for maintenance.
Applicable scenarios:
Centrifugal compressors are suitable for large natural gas stations, especially when large flows and high pressures are required, such as natural gas compression in cross-border gas pipelines.
Key factors for selecting compressor types
When choosing the type of compressor for a natural gas standard station, decisions must be made based on the following factors:
Gas flow and pressure requirements: Select the appropriate type of compressor based on the flow and pressure requirements of natural gas. The piston type is suitable for small and medium-sized sites, the screw type is suitable for medium-sized sites, and the centrifugal type is suitable for large sites.
Equipment operation stability: The selected natural gas standard station compressor should have the ability to operate stably for a long time to ensure the continuous supply of natural gas.
Maintenance and cost: When selecting a natural gas standard station compressor, the maintenance cost and overall investment of the equipment must also be considered. Different types of natural gas standard station compressors vary in cost and maintenance, and selection needs to be made according to specific circumstances.
Conclusion
As an important equipment in the natural gas transmission system, the type of natural gas standard station compressor directly affects the operating efficiency and stability of the system. In the natural gas standard station, piston, screw and centrifugal compressors each have their own advantages and disadvantages. The selection of the appropriate type of natural gas compressor should be based on multiple considerations such as flow, pressure, stability and cost. With the development of science and technology, the natural gas standard station compressors technology will also be more efficient and environmentally friendly, providing a stronger guarantee for the safe and stable transportation of natural gas.